Investigating the Interplay between Market Volatility, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), and the Nigerian Economy amidst the Covid-19 Pandemic.
This study investigates the relationship between market volatility and foreign direct investment (FDI) in Nigeria during the covid-19 pandemic. It further examines the impact of the pandemic on capital market returns and the manufacturing sector.
The E-views software was used to measure the volatility of the chosen dependent variable amidst COVID-19. The log of the variance series was used which is usually stationary to perform the EGARCH (Exponential, Generalized, Autoregressive, Conditional Heteroscedasticity models for volatility clustering), tests analysis.
The choice of this framework is to capture the leverage effect of shocks (policies, incidents, major events, and news) on the financial market
Steps to run the EGARCH analysis:
load data
plot series for visualization (histogram)
the data should be stationary using the ADF test (Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test)
test for ARCH effect using OLS (there should be volatility clustering)
if present, estimate the ARCH model by the maximum likelihood method
estimate exponential GARCH model (EGARCH)
interpret results and run a diagnosis
The images below are research findings, showing descriptive statistics, data visualization, ARCH, and heteroscedasticity, this test is to evaluate stationary and volatility clustering. Presenting the econometric result of EGARCH analysis which enabled me to decide the leverage and volatility effect of COVID-19 on the respective variables.
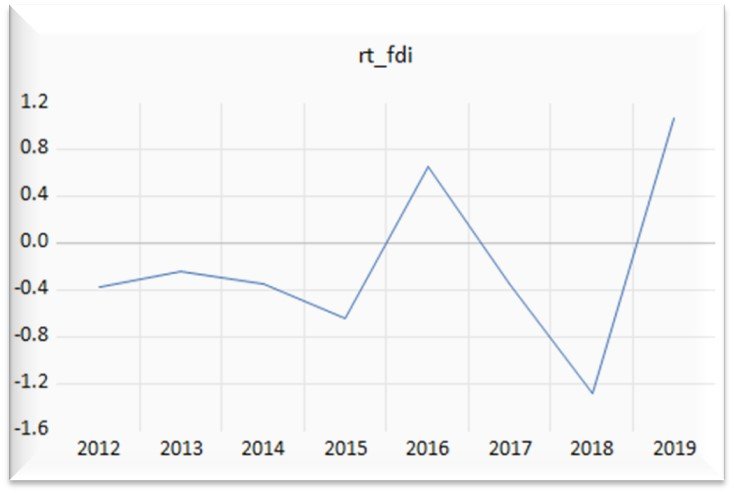



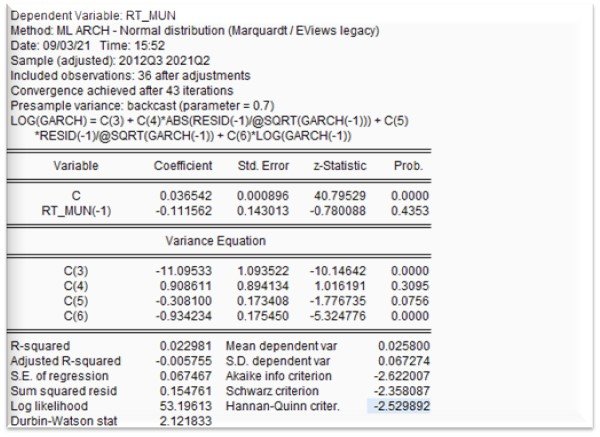

Key Findings:
Manufacturing sector - Market volatility (negative shocks) significantly hampered the returns of manufacturing companies (beverages & food) during COVID-19. This suggests bad news has a stronger impact on this sector compared to positive news.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) - the study found no significant effect of COVID-19 on FDI. Interestingly, a major PE transaction occurred during this period, indicating positive industry prospects. This suggests good news has a stronger impact on FDI than bad news.
Market Volatility - The study reveals persistent market volatility with a tendency for "clustering" (periods of high or low volatility following each other).
Investment Strategy - Based on the findings, the author encourages investors to continue with FDI in Nigeria, either reinvesting in existing companies or acquiring new ones.
Regulatory Role - The study suggests that regulatory authorities should increase market surveillance to mitigate investor concerns and prevent panic due to volatility.
Overall, the study highlights the contrasting impacts of COVID-19 on the manufacturing sector (negatively affected by volatility) and FDI (relatively unaffected). I recommended continued investment in Nigeria while advocating for stronger regulatory oversight to manage market volatility.
To see full project click here